Covered put option example
Founded in by brothers Tom and David Gardner, The Motley Fool helps millions of people attain financial freedom through our website, podcasts, books, newspaper column, radio show, and premium investing services.
There are plenty of ways to profit on a stock's movement, beyond investing in the actual stock itself.

Options provide a nearly endless array of strategies, due to the countless ways you can combine buying and selling call option s and put option s at different strike prices and expirations. A call is an options contract that gives the owner the right to purchase the underlying security at the specified strike price at any point up until expiration.
A put is an options contract that gives the owner the right to sell the underlying asset at the specified strike price at any point up until expiration. A fairly basic position is the covered put, which is very similar strategically to a covered call.
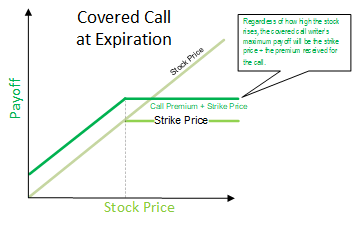
A covered put is a bearish strategy that is essentially a short version of the covered call.
In a covered put, if you have a negative outlook on the stock and are interested in shorting it, you can combine a short stock position with a short put position.
This creates some immediate income upfront from the premium received from writing the put. It also limits your potential gain on the short position, since if the stock decreases to below the put's strike price, you will subsequently purchase the shares through the option exercise and close out your short position. There is no theoretical limit to how much you can potentially lose on a covered put. This is due to the fact that stocks do not have a maximum limit, and a stock can continue rising against a short position.
This unlimited maximum loss is also true for any short stock position; a short put would only merely offset losses by a small amount in the short stock position should the stock increase in price. Of course, in reality stock prices don't increase to infinity, so this risk is purely hypothetical. The most that you can make on a covered put position is the difference between the option strike price and the price that you shorted the stock, plus any premium received.
This occurs if the stock declines to a price less than or equal to the put strike price, in which case the option is exercised and you purchase the stock at the strike price and cover your short position.
The breakeven point for a covered put is the cost basis of the short position plus the premium received.
If the stock price begins to increase, the short stock position begins to lose value, but the premium received will offset these losses to a point.
If the stock increases above this point, then you begin to accrue losses. Much like a covered call position, which is a popular income-generating position among options investors, a covered put can also generate income. If the put expires worthless and you keep the premium received as realized gains, you can choose to sell another put and repeat the process provided that you are still comfortable holding the short stock position.
Using Covered Calls and Covered Puts to Manage Risk
Try any of our Foolish newsletter services free for 30 days. We Fools may not all hold the same opinions, but we all believe that considering a diverse range of insights makes us better investors. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
Put Option Explained | Online Option Trading Guide
Skip to main content The Motley Fool Fool. Premium Advice Help Fool Answers Contact Us Login.
Latest Stock Picks Stocks Premium Services. Stock Advisor Flagship service. Rule Breakers High-growth stocks. Income Investor Dividend stocks.
Hidden Gems Small-cap stocks. Inside Value Undervalued stocks. Learn How to Invest. Credit Cards Best Credit Cards of Best Credit Card Sign-Up Bonuses Best Balance-Transfer Credit Cards Best Travel Credit Cards Best Cash-Back Credit Cards Best No-Annual-Fee Credit Cards Best Small Business Credit Cards.
Mortgages Compare Mortgage Rates Get Pre-Approved How Much House Can I Afford?
Taxes How to Reduce Your Taxes Deductions Even Pros Overlook Audit-Proof Your Tax Return What Info Should I Keep? Helping the World Invest — Better. How to Invest Learn How to Invest. Personal Finance Credit Cards Best Credit Cards of Best Credit Card Sign-Up Bonuses Best Balance-Transfer Credit Cards Best Travel Credit Cards Best Cash-Back Credit Cards Best No-Annual-Fee Credit Cards Best Small Business Credit Cards.
What Is a Covered Put? Here's the basic setup of a covered put, along with how to calculate the position's maximum gain, maximum loss, and breakeven point. The basic setup A covered put is a bearish strategy that is essentially a short version of the covered call.
How to Invest in Options. Prev 1 2 3 4 Next.